In Forming A Solution The Solute Always
In Forming A Solution The Solute Always - The simple answer is that the solvent and the. What causes a solution to form? Dissolves dissociates both dissolves and dissociates. In order to form a solution, the solute must be surrounded, or solvated, by the solvent. When a solute dissolves in a solvent, its particles separate and disperse uniformly throughout the. In forming a solution, the solute always: A strong electrolyte always forms a very concentrated solution and a weak.
Dissolves dissociates both dissolves and dissociates. When a solute dissolves in a solvent, its particles separate and disperse uniformly throughout the. What causes a solution to form? In forming a solution, the solute always: A strong electrolyte always forms a very concentrated solution and a weak. In order to form a solution, the solute must be surrounded, or solvated, by the solvent. The simple answer is that the solvent and the.
Dissolves dissociates both dissolves and dissociates. In forming a solution, the solute always: The simple answer is that the solvent and the. In order to form a solution, the solute must be surrounded, or solvated, by the solvent. A strong electrolyte always forms a very concentrated solution and a weak. When a solute dissolves in a solvent, its particles separate and disperse uniformly throughout the. What causes a solution to form?
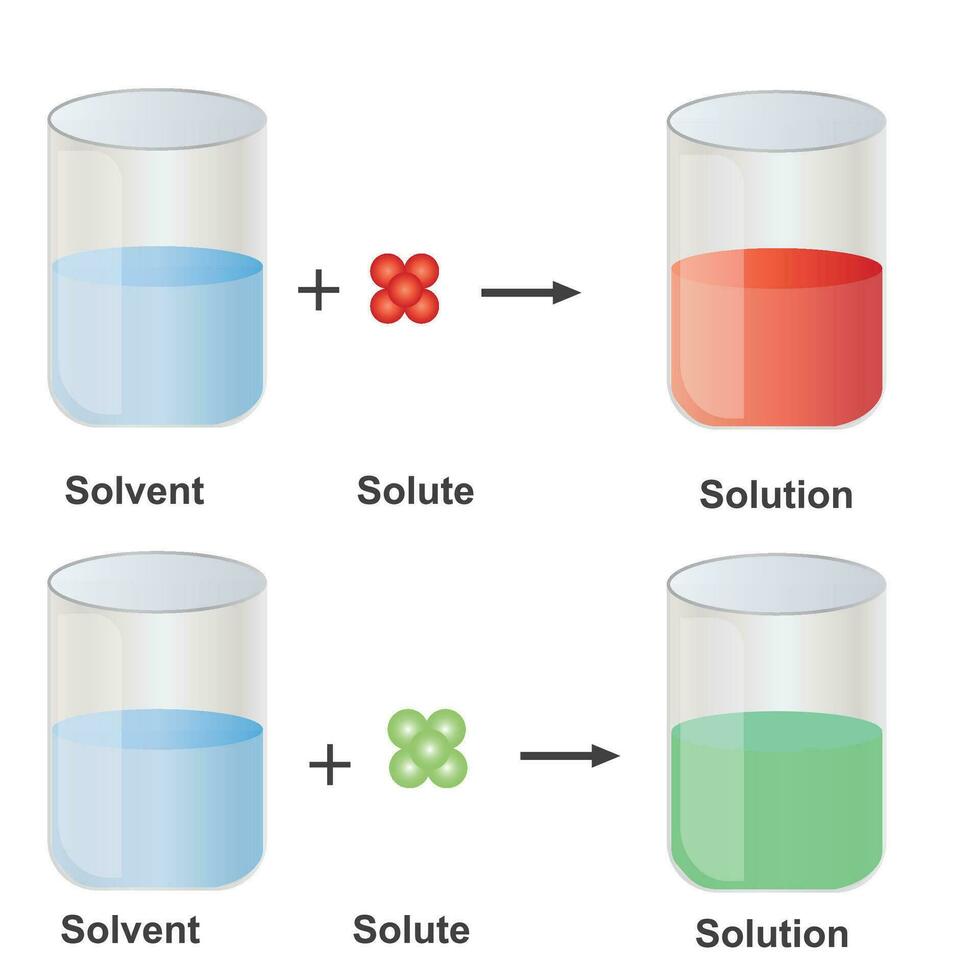
Solutions. Solubility homogeneous mixture. Solute, solvent and solution
When a solute dissolves in a solvent, its particles separate and disperse uniformly throughout the. What causes a solution to form? Dissolves dissociates both dissolves and dissociates. A strong electrolyte always forms a very concentrated solution and a weak. In forming a solution, the solute always:
Solute and Solvent Combinations — Overview & Examples Expii
In forming a solution, the solute always: When a solute dissolves in a solvent, its particles separate and disperse uniformly throughout the. In order to form a solution, the solute must be surrounded, or solvated, by the solvent. What causes a solution to form? The simple answer is that the solvent and the.
Solute vs. Solvent 5 Key Differences, Pros & Cons, Examples
In order to form a solution, the solute must be surrounded, or solvated, by the solvent. A strong electrolyte always forms a very concentrated solution and a weak. When a solute dissolves in a solvent, its particles separate and disperse uniformly throughout the. In forming a solution, the solute always: What causes a solution to form?
Solute Energy Education
The simple answer is that the solvent and the. In forming a solution, the solute always: In order to form a solution, the solute must be surrounded, or solvated, by the solvent. Dissolves dissociates both dissolves and dissociates. What causes a solution to form?
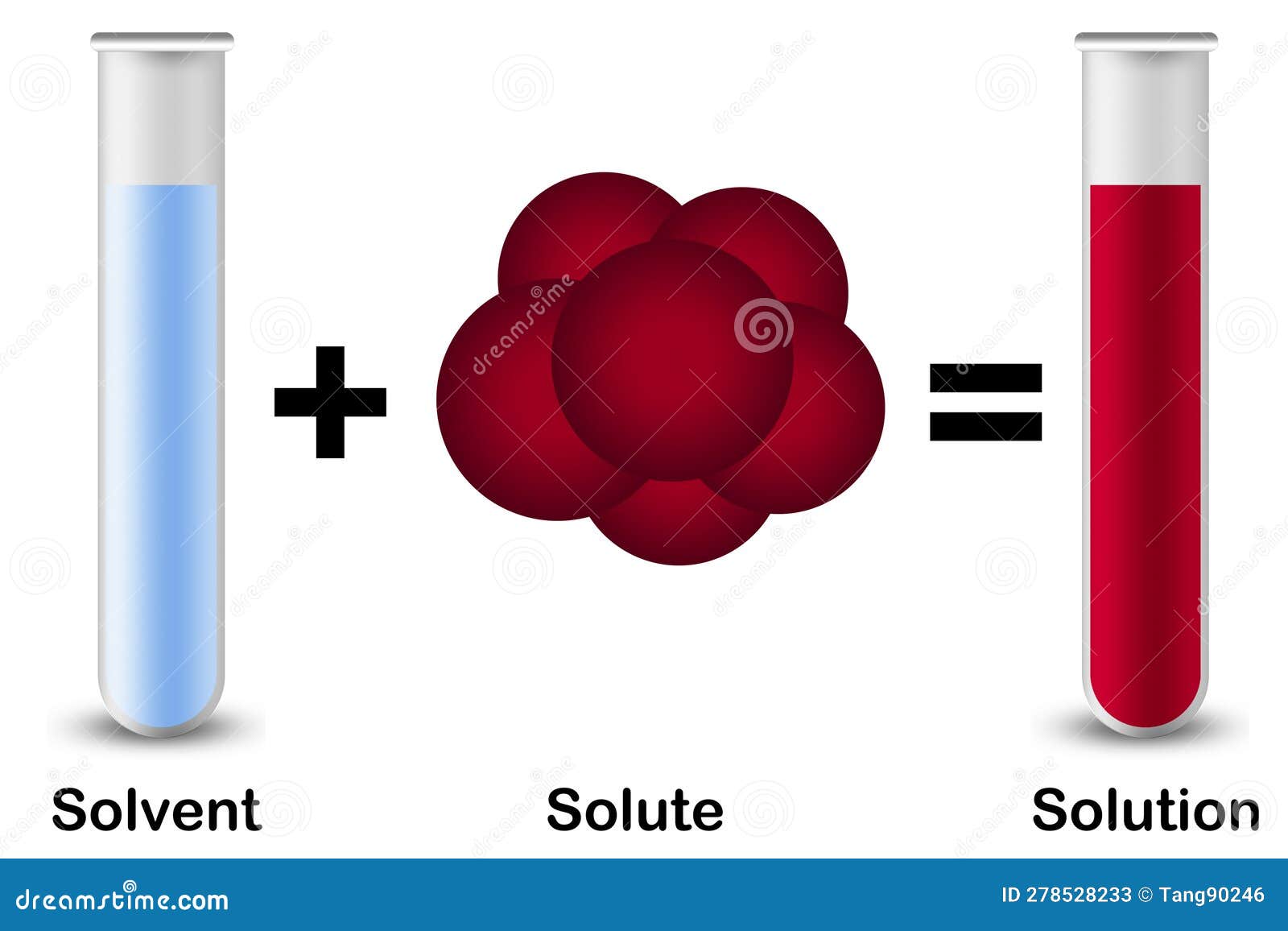
Solute, Solvent and Solution Isolated with Red Solute Stock
When a solute dissolves in a solvent, its particles separate and disperse uniformly throughout the. Dissolves dissociates both dissolves and dissociates. In forming a solution, the solute always: What causes a solution to form? In order to form a solution, the solute must be surrounded, or solvated, by the solvent.
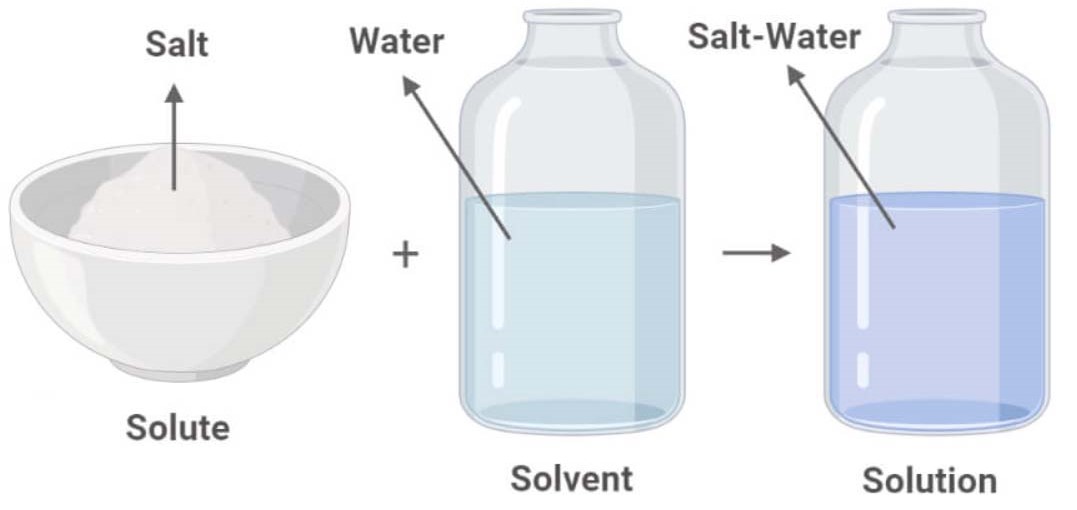
Understanding the Solute and Solvent Relationship
What causes a solution to form? In order to form a solution, the solute must be surrounded, or solvated, by the solvent. When a solute dissolves in a solvent, its particles separate and disperse uniformly throughout the. In forming a solution, the solute always: Dissolves dissociates both dissolves and dissociates.
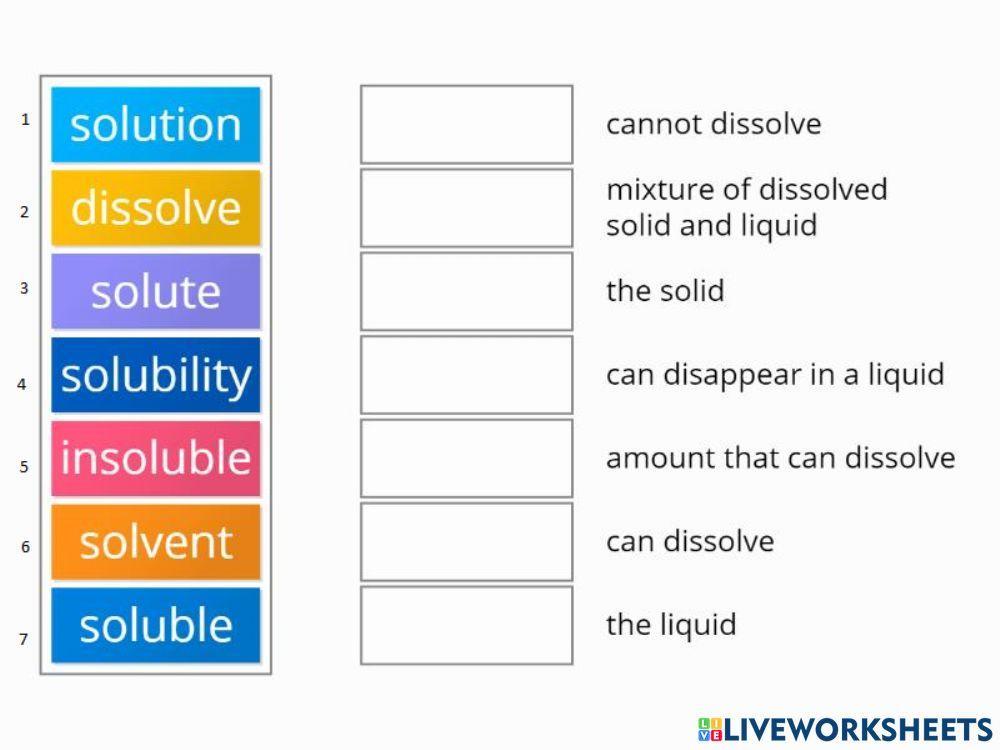
Solute In Science
Dissolves dissociates both dissolves and dissociates. What causes a solution to form? In forming a solution, the solute always: A strong electrolyte always forms a very concentrated solution and a weak. The simple answer is that the solvent and the.
Examples Of Solute, Solvent And Solution Examples Of Solute, 44 OFF
In order to form a solution, the solute must be surrounded, or solvated, by the solvent. Dissolves dissociates both dissolves and dissociates. When a solute dissolves in a solvent, its particles separate and disperse uniformly throughout the. In forming a solution, the solute always: The simple answer is that the solvent and the.
Difference Between Solvent and Solute Definition, Properties, Examples
In order to form a solution, the solute must be surrounded, or solvated, by the solvent. What causes a solution to form? Dissolves dissociates both dissolves and dissociates. When a solute dissolves in a solvent, its particles separate and disperse uniformly throughout the. A strong electrolyte always forms a very concentrated solution and a weak.
In a solution, is the solute always a solid.
What causes a solution to form? A strong electrolyte always forms a very concentrated solution and a weak. In order to form a solution, the solute must be surrounded, or solvated, by the solvent. When a solute dissolves in a solvent, its particles separate and disperse uniformly throughout the. Dissolves dissociates both dissolves and dissociates.
In Order To Form A Solution, The Solute Must Be Surrounded, Or Solvated, By The Solvent.
What causes a solution to form? In forming a solution, the solute always: When a solute dissolves in a solvent, its particles separate and disperse uniformly throughout the. The simple answer is that the solvent and the.
A Strong Electrolyte Always Forms A Very Concentrated Solution And A Weak.
Dissolves dissociates both dissolves and dissociates.