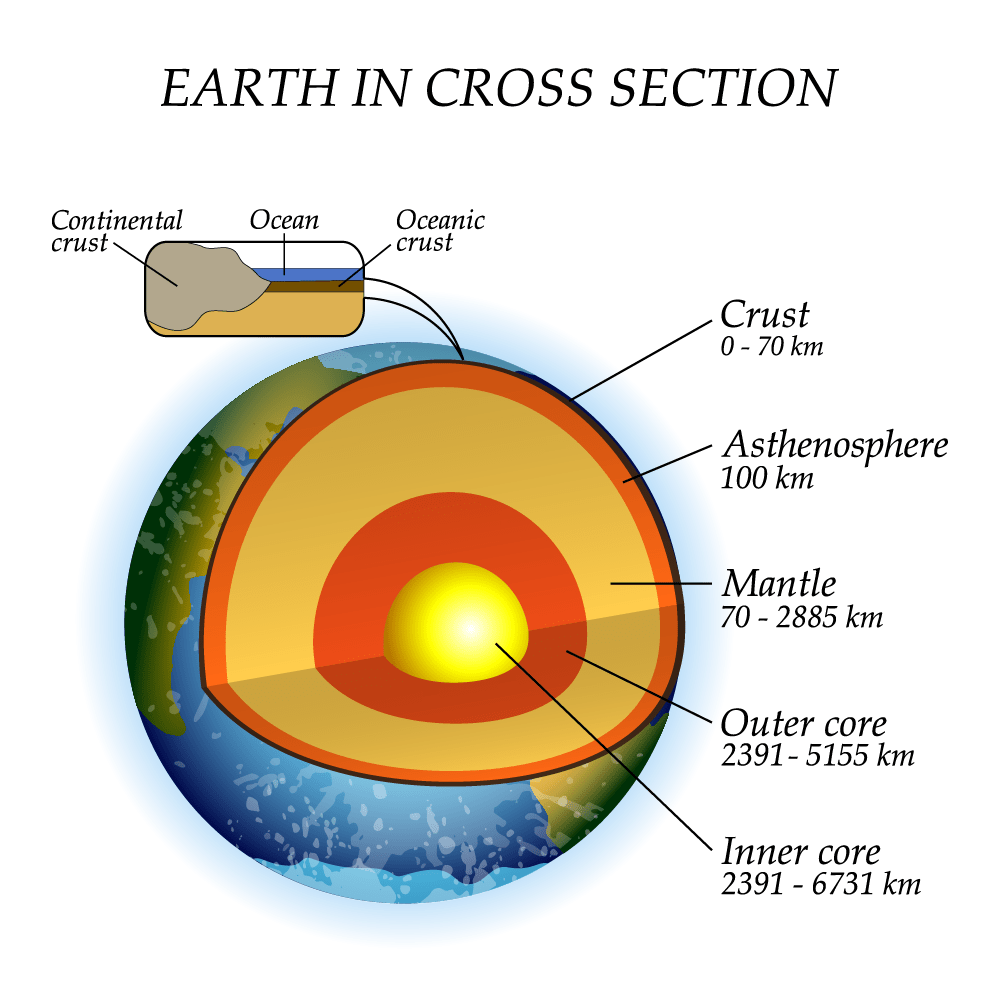
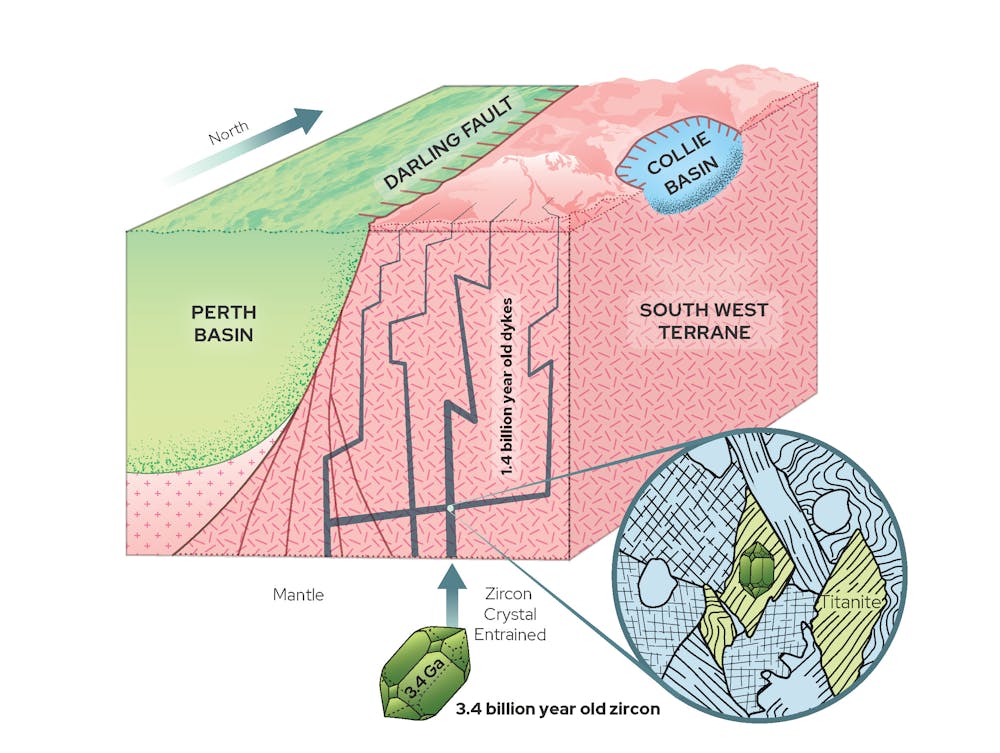
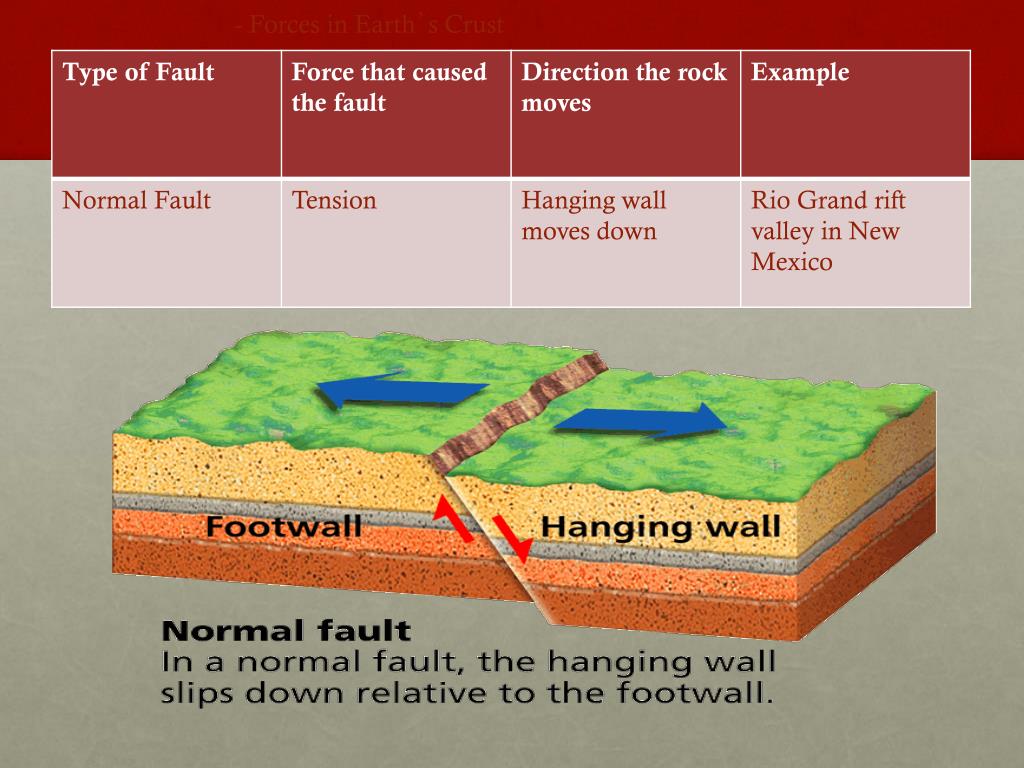
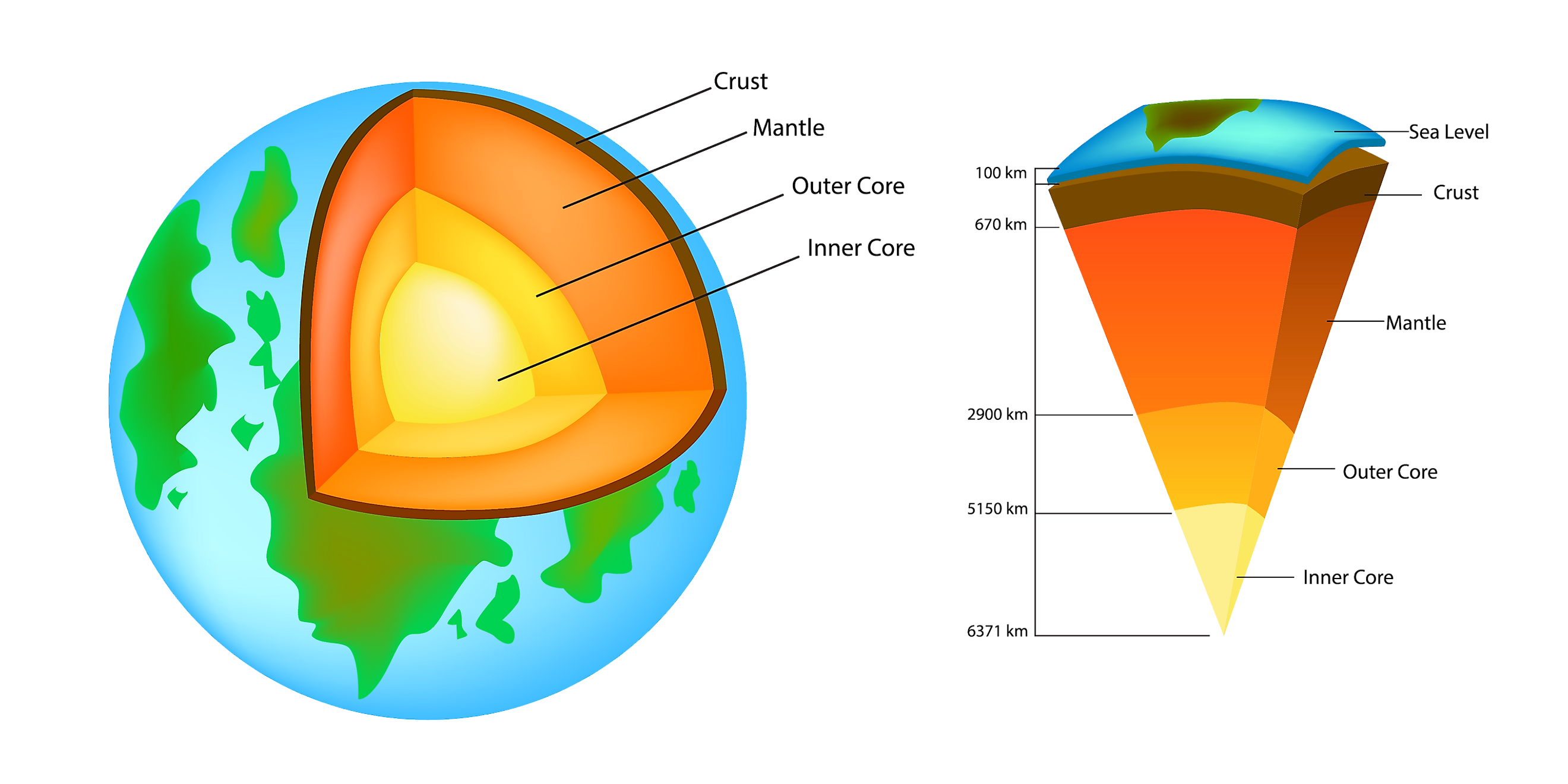
Folds In The Earth S Crust Form Mostly
Folds In The Earth S Crust Form Mostly - Folding is a product of the collision between two tectonic plates that causes the crust to rise up in folds during or after an earthquake. By studying folds, geologists gain. Folding is one of the endogenetic processes; Folds in rocks vary in size from microscopic crinkles to. They are windows into the planet’s dynamic history. The primary cause of folds in the earth's crust is lithospheric plate movement, which is governed by tectonic forces. It takes place within the earth's crust. Folds are more than just bends in the earth’s crust;
They are windows into the planet’s dynamic history. Folds in rocks vary in size from microscopic crinkles to. The primary cause of folds in the earth's crust is lithospheric plate movement, which is governed by tectonic forces. Folds are more than just bends in the earth’s crust; It takes place within the earth's crust. Folding is one of the endogenetic processes; Folding is a product of the collision between two tectonic plates that causes the crust to rise up in folds during or after an earthquake. By studying folds, geologists gain.
The primary cause of folds in the earth's crust is lithospheric plate movement, which is governed by tectonic forces. By studying folds, geologists gain. Folds in rocks vary in size from microscopic crinkles to. Folds are more than just bends in the earth’s crust; Folding is one of the endogenetic processes; It takes place within the earth's crust. They are windows into the planet’s dynamic history. Folding is a product of the collision between two tectonic plates that causes the crust to rise up in folds during or after an earthquake.
Deformation Of The Earth S Crust Is Called Quizlet The Earth Images
It takes place within the earth's crust. Folding is one of the endogenetic processes; Folding is a product of the collision between two tectonic plates that causes the crust to rise up in folds during or after an earthquake. By studying folds, geologists gain. The primary cause of folds in the earth's crust is lithospheric plate movement, which is governed.
The Running Scientist Folds in the Earth's Crust
Folds are more than just bends in the earth’s crust; Folds in rocks vary in size from microscopic crinkles to. They are windows into the planet’s dynamic history. Folding is a product of the collision between two tectonic plates that causes the crust to rise up in folds during or after an earthquake. It takes place within the earth's crust.
PPT Forces in Earth’s crust PowerPoint Presentation, free download
Folding is a product of the collision between two tectonic plates that causes the crust to rise up in folds during or after an earthquake. Folds in rocks vary in size from microscopic crinkles to. The primary cause of folds in the earth's crust is lithospheric plate movement, which is governed by tectonic forces. They are windows into the planet’s.
Folds Occurring Earths Crust Due Side Stock Illustration 1092702176
Folding is a product of the collision between two tectonic plates that causes the crust to rise up in folds during or after an earthquake. The primary cause of folds in the earth's crust is lithospheric plate movement, which is governed by tectonic forces. Folds are more than just bends in the earth’s crust; It takes place within the earth's.
Folds, Faults, and the Deformation of Earth`s Crust
By studying folds, geologists gain. Folding is a product of the collision between two tectonic plates that causes the crust to rise up in folds during or after an earthquake. It takes place within the earth's crust. Folds are more than just bends in the earth’s crust; The primary cause of folds in the earth's crust is lithospheric plate movement,.
Unveiling Ancient Earth Discovering Remnants Of Primordial Crust
Folding is a product of the collision between two tectonic plates that causes the crust to rise up in folds during or after an earthquake. Folding is one of the endogenetic processes; Folds are more than just bends in the earth’s crust; The primary cause of folds in the earth's crust is lithospheric plate movement, which is governed by tectonic.
geology Do earthquakes produce folds on rocks? Earth Science Stack
Folding is a product of the collision between two tectonic plates that causes the crust to rise up in folds during or after an earthquake. Folds are more than just bends in the earth’s crust; Folding is one of the endogenetic processes; By studying folds, geologists gain. They are windows into the planet’s dynamic history.
Illustration of folds forming in the Earths crust For sale as Framed
It takes place within the earth's crust. Folding is one of the endogenetic processes; Folds in rocks vary in size from microscopic crinkles to. Folds are more than just bends in the earth’s crust; They are windows into the planet’s dynamic history.
What Causes Faults In Earth S Crust The Earth Images
The primary cause of folds in the earth's crust is lithospheric plate movement, which is governed by tectonic forces. Folding is one of the endogenetic processes; Folding is a product of the collision between two tectonic plates that causes the crust to rise up in folds during or after an earthquake. By studying folds, geologists gain. Folds are more than.
The Most Abundant Elements In The Earth's Crust WorldAtlas
Folding is a product of the collision between two tectonic plates that causes the crust to rise up in folds during or after an earthquake. The primary cause of folds in the earth's crust is lithospheric plate movement, which is governed by tectonic forces. Folds are more than just bends in the earth’s crust; By studying folds, geologists gain. It.
The Primary Cause Of Folds In The Earth's Crust Is Lithospheric Plate Movement, Which Is Governed By Tectonic Forces.
By studying folds, geologists gain. Folds are more than just bends in the earth’s crust; They are windows into the planet’s dynamic history. It takes place within the earth's crust.
Folding Is One Of The Endogenetic Processes;
Folds in rocks vary in size from microscopic crinkles to. Folding is a product of the collision between two tectonic plates that causes the crust to rise up in folds during or after an earthquake.